Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are important parts that are embedded in diverse things related to our lives, such as personal electronic devices: personal computers and smartphones, as well as automobiles and aircraft. Printed circuit boards have a multi-layered structure that allows fine wiring to be drawn, contributing to the miniaturization of electronic devices.
This column explains what a printed circuit board is, its benefits, and types.
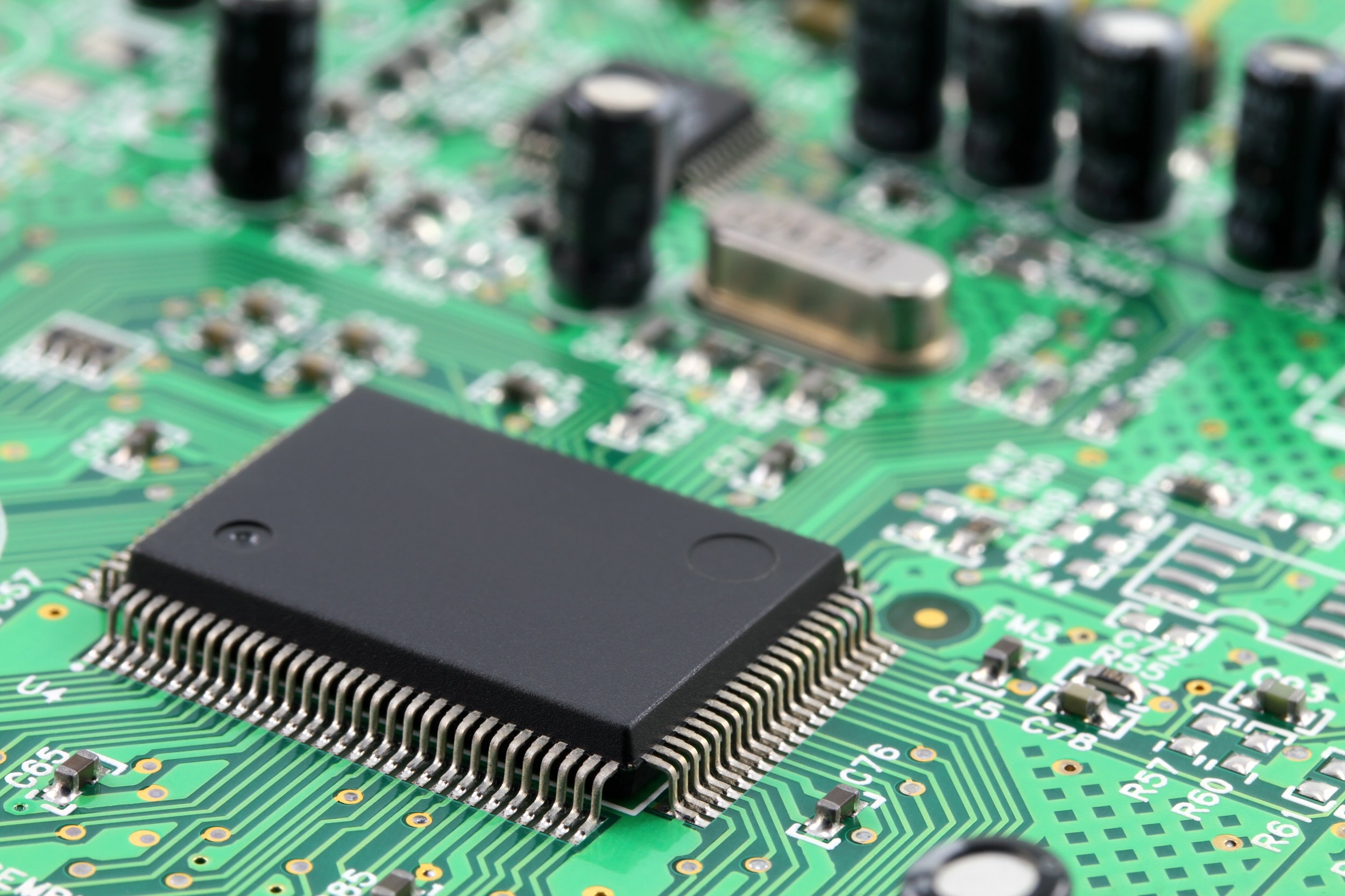

What is a printed circuit board that supports electronic circuits?
A printed circuit board is a part that is embedded in almost all electronic devices and is essential for the design of electronic circuits. A printed circuit board is generally a green plate-shaped part made of an insulator, and copper foil is used for wiring on its surface and inside. An electronic circuit is completed by soldering many electronic parts such as semiconductors, capacitors, and connectors to the surface.
- Benefits of Printed Circuit Boards
Contributing to miniaturization and mass production of electronic devices
In order to realize complex wiring in the minimum space, printed circuit boards has many traces on its inner layers and on its surface. Since compact electronic circuits can be produced, it contributes to the miniaturization of electronic devices. In addition, the use of printed circuit boards streamlines the production of electronic devices and enables mass production.
Types of Printed Circuit Boards: Classify by circuit layer
There are many types of printed circuit boards, but they can be classified according to the circuit layer as follows.
- Single-layer board
A wiring circuit is formed on only one side of a printed circuit board. Since the wiring circuit is on either the front or the back side of the printed circuit board, it is impossible to construct complicated electronic circuits, but it is possible to mass-produce it at a low manufacturing cost.
Single-sided boards are mainly used for large home appliances.
- Double-layer board
A wiring circuit is formed on both the front and back sides of a printed circuit board. Since electronic circuits can be formed on both sides, it is possible to create more complex wiring, such as connecting the wiring on both sides in three dimensions using through-holes, etc.
Since fine electronic circuits can be made, it is used in electronic devices that require miniaturization.
- Multilayer board
It refers to a board with three or more layers of insulators and circuits stacked on top of each other. In addition to the front and back sides, wiring can also be done inside the layer, so it is used for personal computers, smartphones, and other small and highly functional devices that require a lot of wiring.
Types of Printed Circuit Boards: Classify by material
Printed circuit boards can also be classified according to the material from which they are made as follows.
- Rigid board
It is a high-strength board made of a hard insulator such as glass-filled epoxy resin. Benefits of rigid board is able easy to mount components because the rigid board can be fixed directly to the component mounter.
- Flexible wiring board
It is a soft substrate made of insulating materials such as polyimide resin and liquid crystal polymer resin, which are thin and highly flexible.
Its major benefit is that it can be bent and twisted to change its shape, and it is used in a wide range of devices such as small electronic devices that require space saving.
- Rigid flexible printed wiring board
This is a composite board that combines the benefits of a rigid board and a flexible wiring board. It combines the benefits of the ease of parts mounting of a rigid board and the ease of bending of a flexible wiring board.
What is Yamaichi Electronics' flexible wiring board, YFLEX®?
Yamaichi Electronics manufactures and sells YFLEX® as one of the thin flexible wiring board. We are developing YFLEX® that can be used in a variety of ways to meet customer needs, such as electronic devices that requires space saving and equipment that can withstand environments such as noise, high temperatures, and oil.
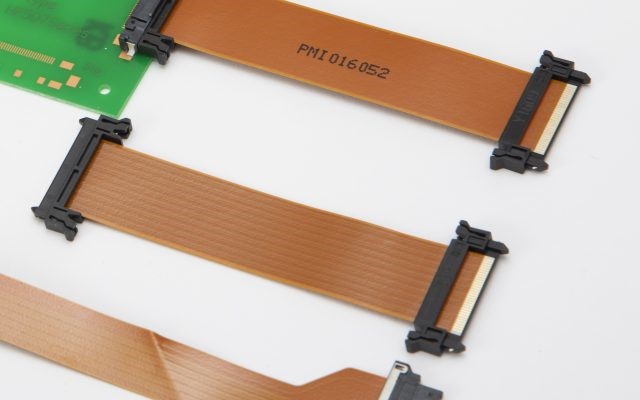

Three main uses of YFLEX® are introduced below.
- Highspeed transmission
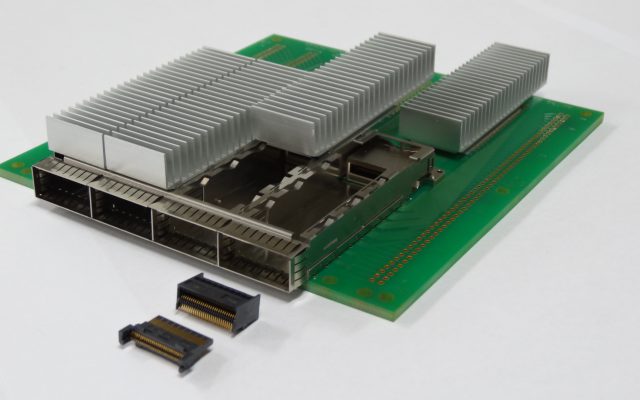
YFLEX® can be used in situations where 56Gbps class high-speed transmission is required from optical modules in communication network equipment to CPUs. It can be used for high-speed transmission in the 28Gbps and 56Gbps classes and for antenna substrates, supporting the field of communication infrastructure.
- Noise resistant applications
We also manufacture YFLEX®, which is resistant to diverse types of noise. It is used for wiring areas that are affected by noise generated in electronic devices and have a risk of degradation in transmission quality.
It is possible to design the functions according to the customer’s request, such as “Impedance matching” that equalizes the impedance value of the signal sending side and receiving side in the electric circuit, “low-loss” that reduces the degree of transmission loss in the electric circuit, and “low-crosstalk” the mutual influence of adjacent cables, products that reduce.
- Special use
We provide YFLEX® specialized for the customer’s request, including heater, high heat resistance, oil resistance, ultra-thin, and high-flexibility performance. For example, as a heater, it is used to prevent fogging of camera lenses and to control the temperature of parts such as sensors. In addition, for oil resistance applications, it is used in machine tools in factories where cutting oil, etc. is sprayed.